What is unemployment?
An explanation that it is the number of people without a job, who are actively seeking work (ILO)
Labour force: The number of people in a country that are of working age and are able to work. Employed people + Unemployed People
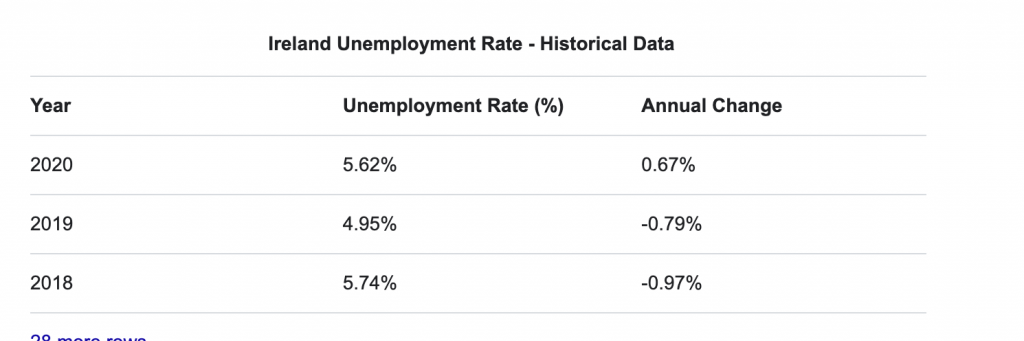
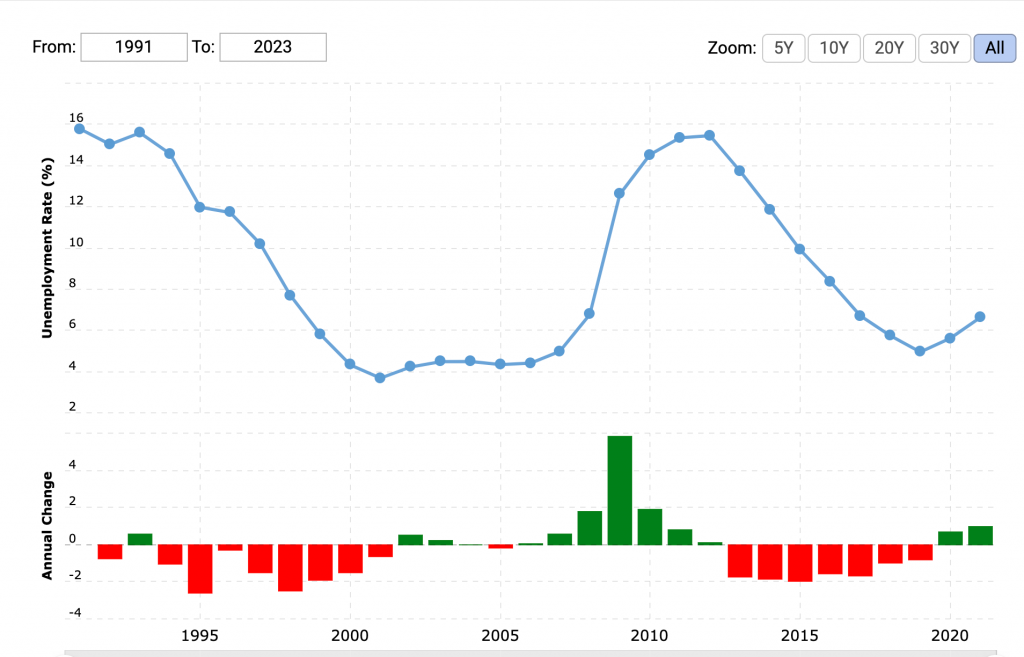
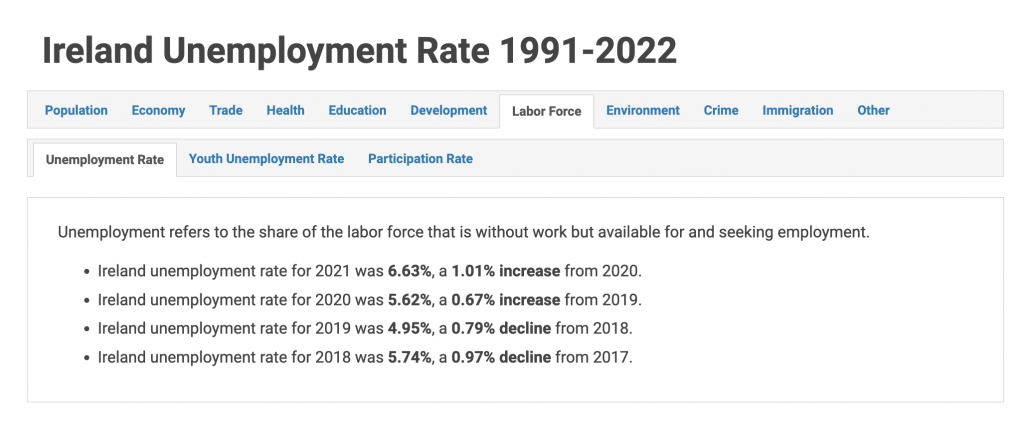
Watch unemployment trends in Ireland – 1990s to 2021
We measure unemployment in Ireland using the Live Register or the Labour Force Survey. Read here for the different between them.
Supply and Demand of Labour
In a free market the demand and supply of labour determines the wage rate. See this post to understand the factors that determine the demand and and supply.
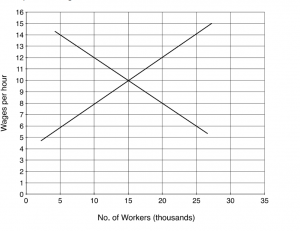
However, government intervention, such as minimum wage can increase the wage rate about market equilibrium rate. See here for the pros and cons of increasing this wage rate.
Mobility of Labour
The easier it is for labour to move to a new job, the lower the level of unemployment. There are two types of mobility:
What are the different types of unemployment?
There are several different types of unemployment, of varying duration and severity (in terms of implications for the economy). This video goes through the types, and addresses why the Macroeconomic goal is “Low Unemployment,” rather than “Zero Unemployment.”
- Cyclical or demand deficient unemployment
- Structural employment
- Seasonal unemployment
- Frictional unemployment
See here for a detailed description for each type of unemployment and the government policies for each type.
Gender Pay Gap
Despite a lot of progress, studies suggest that there is still a 14% difference between male and females workers in Ireland.
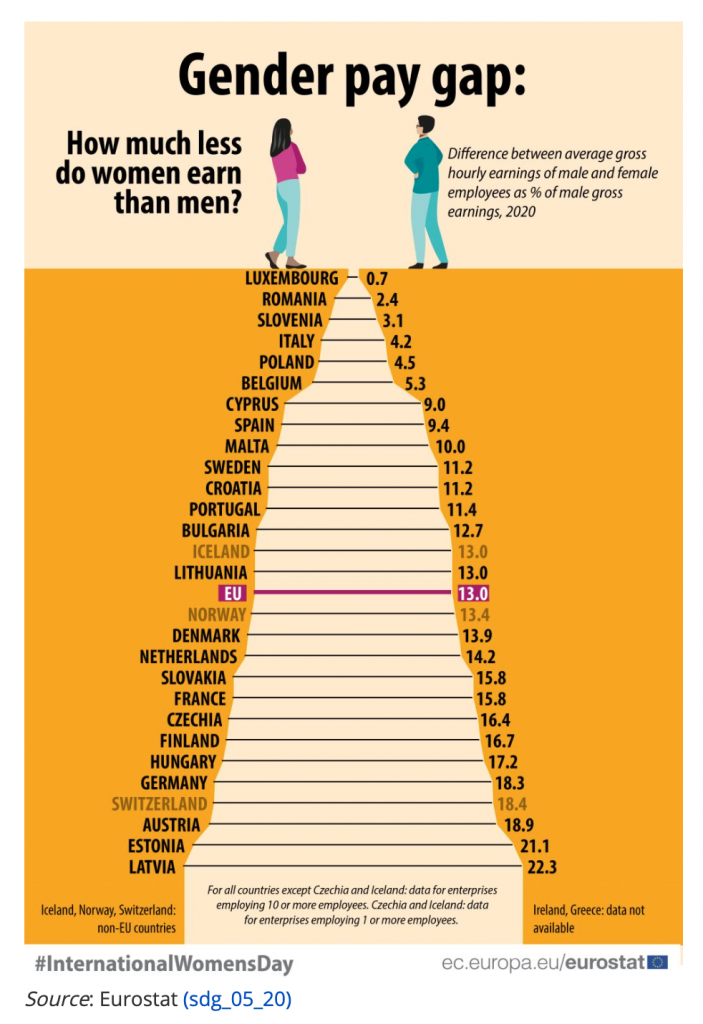
Read here to find out why do women receive lower wages in Ireland?
Read here to for the reasons why workers get paid different wage rates
Implications of unemployment
- The economy – less disposable income, less spending, lower GDP/National income
- Government finances – more spending on social welfare payments
- Households – Emigration rises / brain drain
- Incomes – less income for food, shelter / homes repossessed. Inequalities rise
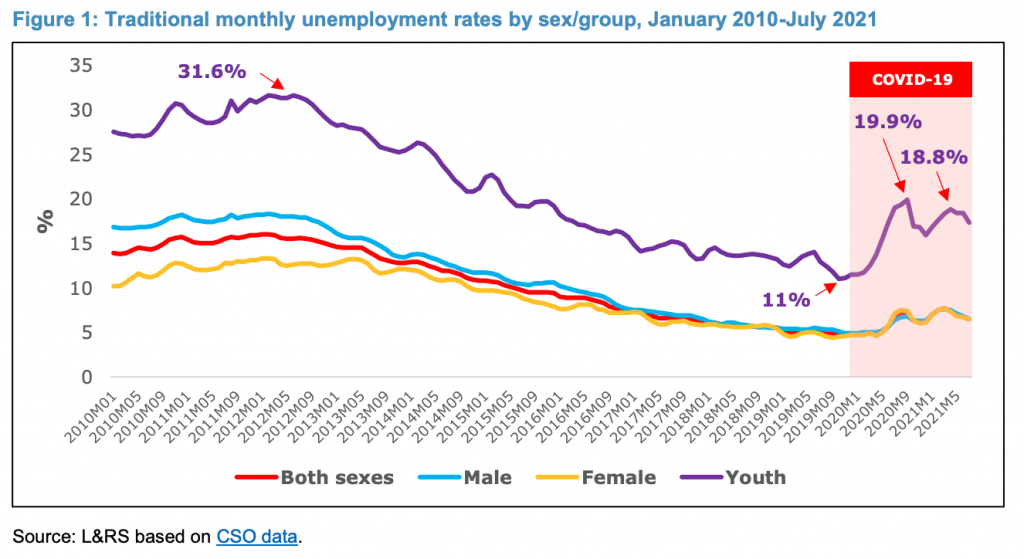
See here for consequences and policies for youth unemployment.
Test your knowledge of low employment