National Income (Y):The income accruing to the permanent residents of a country from current economic activity during a specified period of time, usually a year.
The Central Statistic Office (CSO) is an Irish government body that measures the National Income of Ireland.https://www.cso.ie/en/index.html
It has three’measures available to do it:
1) The Output Method
2) The Expenditure Method
3) The Income Method
Read more about why we use National Income statistics here, as well as the limitations of these statistics.
NATIONAL INCOME= NATIONAL EXPENDITURE = NATIONAL OUTPUT
Double Counting:
The main challenge of measuring National Income (GDP/GNP) is ts to avoid using the same output more than once. total output should equal value of all goods and services produced in the economy, but it is not that simple. if you were to count every good and service produced, that would man that you would end up counting the same output again and again. this would overstate the value of National Income (GDP/GNP)
Measures of Economic Growth
The Three Ways of Measuring Aggregate Demand are:
1) The Aggregate Demand Curve
2) Y = C + I + G + (X – M)
3) The Circular Flow of Income Diagram.
Circular Flow of Income model
The Circular Flow of Income is a diagram of Aggregate Demand. It traces
the flow of the overall money spent in an economy (Aggregate Demand).
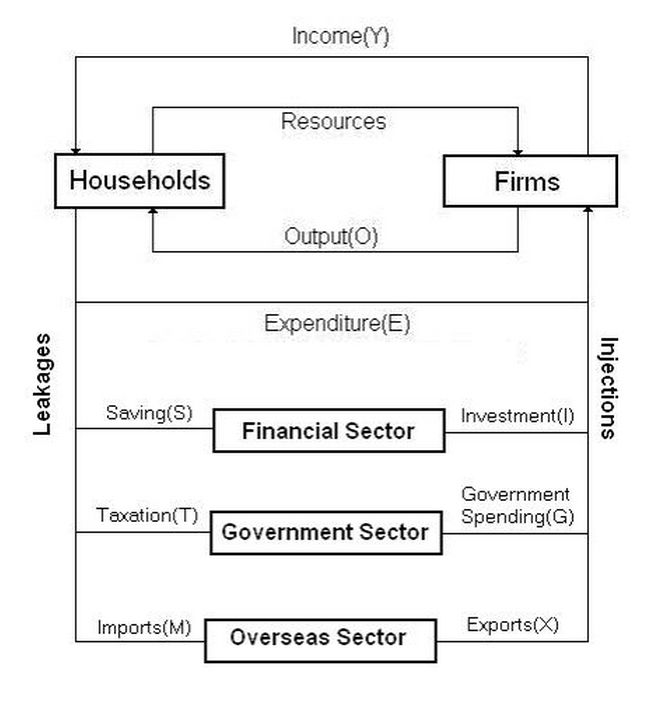
Leakages and Injections
However leakages in the circular flow of income cause income to fall and reduce aggregate demand, while injections cause income to rise and increase aggregate demand.
Leakages: Reduces the flow of income in an economy
- Savings: The proportion of Income not spent. Savings reduces spending within the economy and thereby reduces the Circular Flow of Income.
- Imports: Money spent by Irish citizens on goods and services produced outside of Ireland. Imports reduce the Circular Flow of Income within Ireland.
- Taxes: A contribution required of persons, groups or businesses for the support of the government. It reduces spending within the economy and thus reduces the Circular Flow of Income.
Injections Increases the flow of income in an economy
- Investment: Money spent on Capital goods. It will increase the Circular Flow of Income.
- Exports: Money spent by foreign individuals on goods and services produced within Ireland. It will increase the Circular Flow of Income within Ireland.
- Government Spending: All money spent by the government, both current and capital. It will increase the Circular Flow of Income within Ireland.
- Attempt the following exam questions about circular flow of income
Aggregate Demand
The Multiplier effect
The Multiplier effect: MPS, MPC
The Multiplier: Leakages and Injections
GDP
It is important that you can differentiate between GDP, GNP, GNI and GNDI as measures of national income; and analyse which measure is a more accurate indicator of Ireland’s economic performance and economic welfare. See here for more details.
Business cycle
Read about the different phases of the business cycle here.
Questions
Practice the following questions on National Income.
